Styles
All of the Omni applications are about organizing and presenting data for you to understand, manipulate, control, and share. Presenting the data in attractive formats is essential to the success of those goals. In OmniOutliner, editable style sheets are used to apply text formatting to outline elements.
In an outline document, there are three types of styles:
- Whole Document · Formatting attributes that apply globally to the entire document.
- Level Styles · Formatting that is applied to rows based upon their position in the outline hierarchy.
- Named Styles · Defined formatting sets that are titled and can be applied to ranges of characters.
In this section we’ll examine how to use scripting to read and apply styles, starting with the Whole Document or “base style.”
The Base Style
The base style (baseStyle) is a set of formatting attributes that applies to all text in an outline document. Other styling that supersedes the base style can be applied to text, but if the added styling is cleared or removed, the base style will remain active.
In scripting terms, the “base style” is represented as the value of the baseStyle property belonging to the outline object of the document.
The Base Style Object
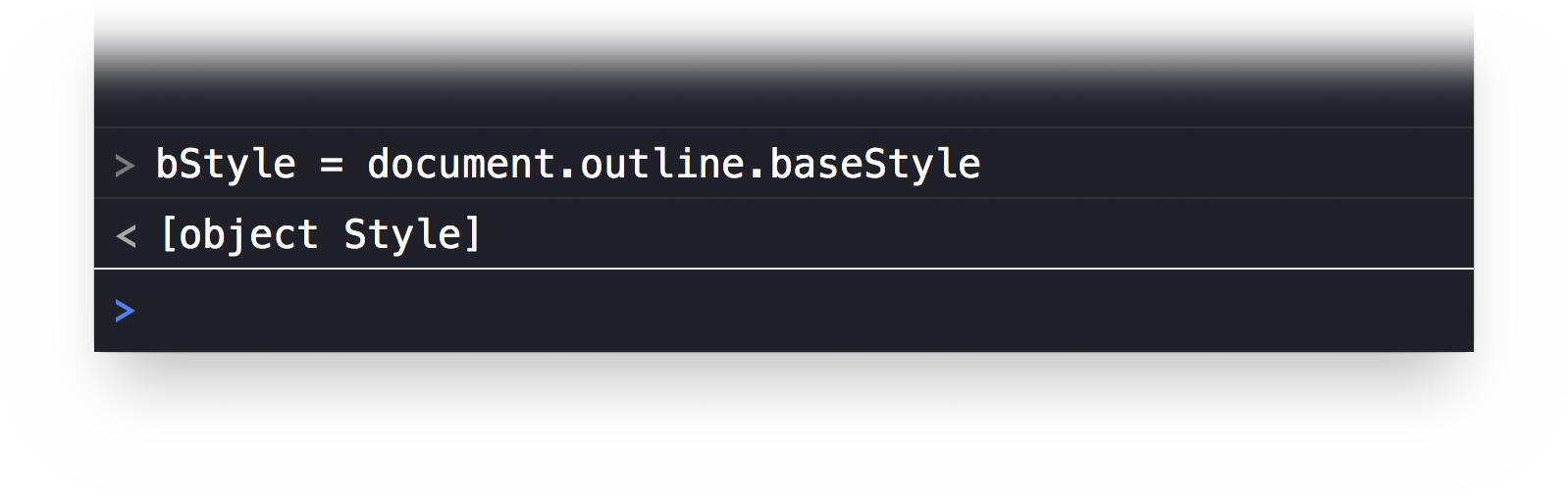
bStyle = document.outline.baseStyle
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script will be the base style object placed into the variable titled: bStyle
Let’s examine some of the current values of the formatting attributes of the base style. To retrieve the value of a style attribute, use the get method on the object reference of the base style stored in the variable from the previous script. This method takes a style attribute as its direct parameter.
In the following example script, the Style.Attribute class is appended with the style property fontFamily to create a reference to a specific style attribute, specifically, the name of the typeface family of the base style.
Value of Style Attribute: Font Family
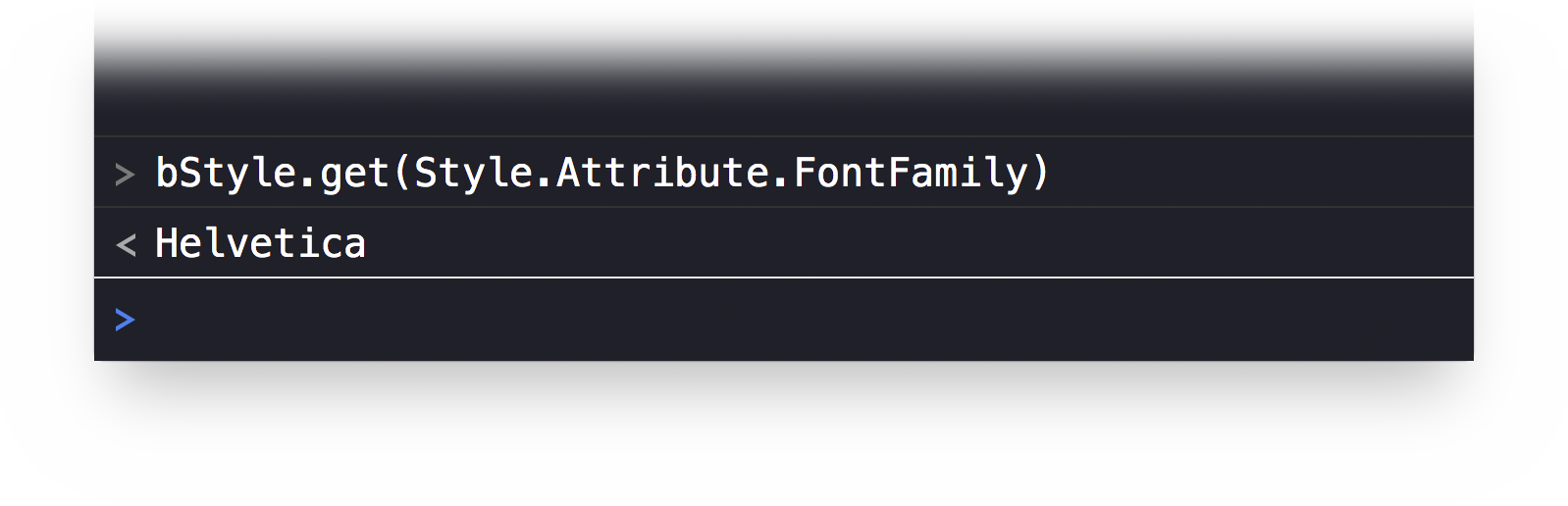
bStyle = document.outline.baseStylebStyle.get(Style.Attribute.FontFamily)
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script will be the name of the font family of the base style: Helvetica
Next, let’s retrieve the value of the FontSize attribute:
Value of Style Attribute: Font Size
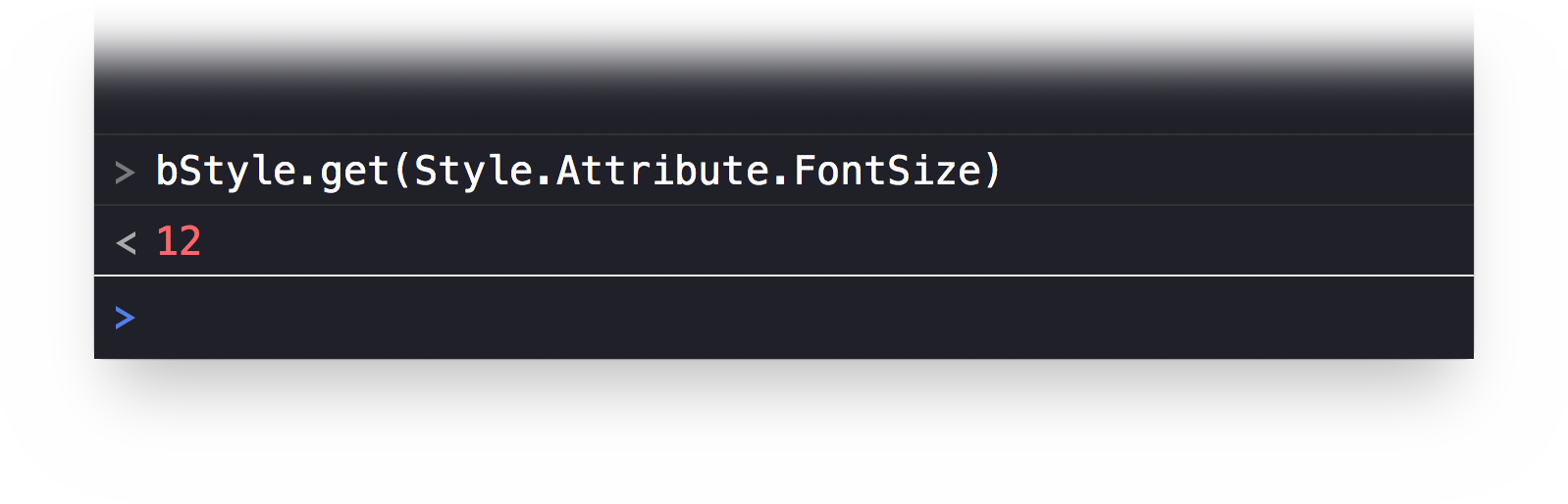
bStyle = document.outline.baseStylebStyle.get(Style.Attribute.FontSize)
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script will be the size of the default font in points: 12
Changing Attribute Values
The value of Style Attributes can be changed using the set() method of the Style class. This method takes two parameters: the style attribute whose value is to be changed, and the new value for the targeted attribute.
Let’s begin by changing the value of the FontSize attribute of the base style.
Set Style Attribute: Font Size
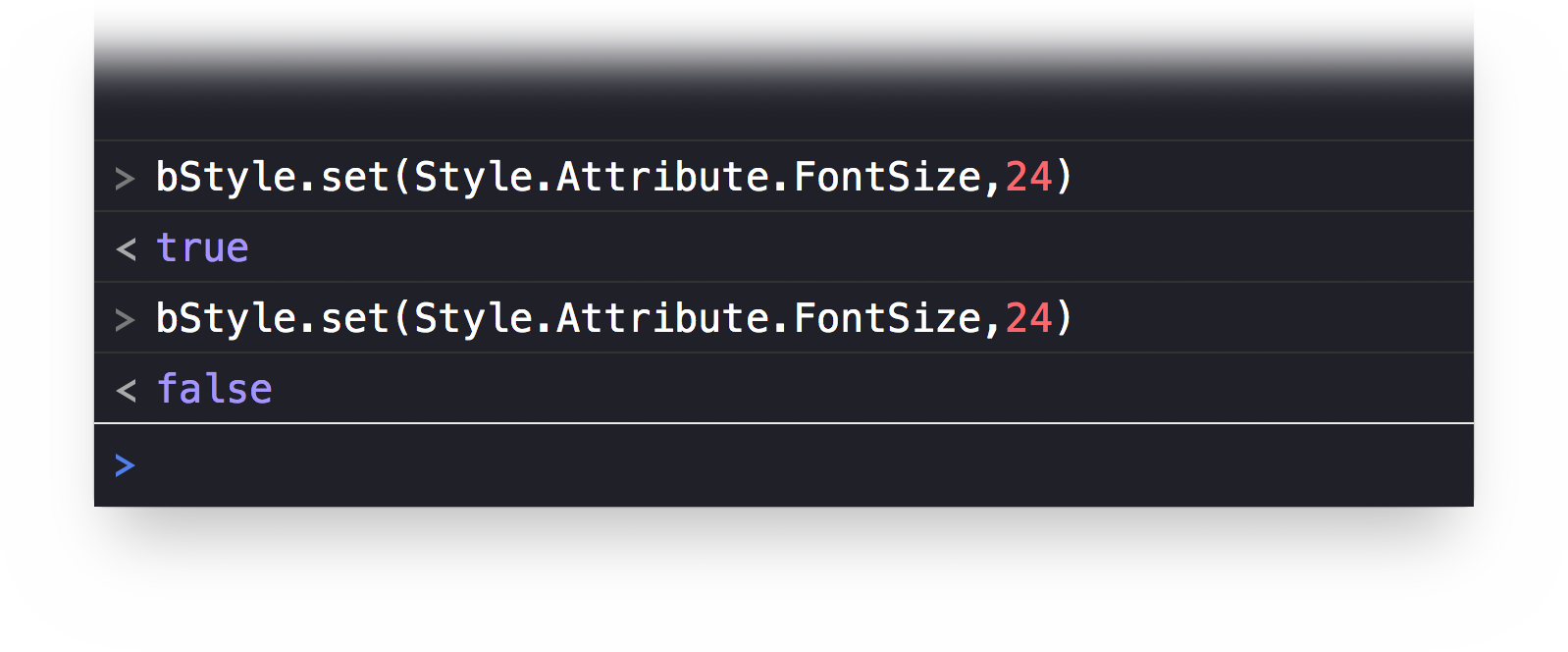
bStyle = document.outline.baseStylebStyle.set(Style.Attribute.FontSize, 24)
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script execution will be a boolean value with true indicating that the change was successfully applied, and false if nothing was changed. If the value of the target attribute is already equal to the new value, nothing will change and false will be returned.
| DO THIS ► | Run the script a second time and note that a value of false is returned. |
Next, let’s change the value of the FontFamily style attribute. Note that the font family is a text string and so must be encased in either single or double quotes.
Set Style Attribute: Font Family
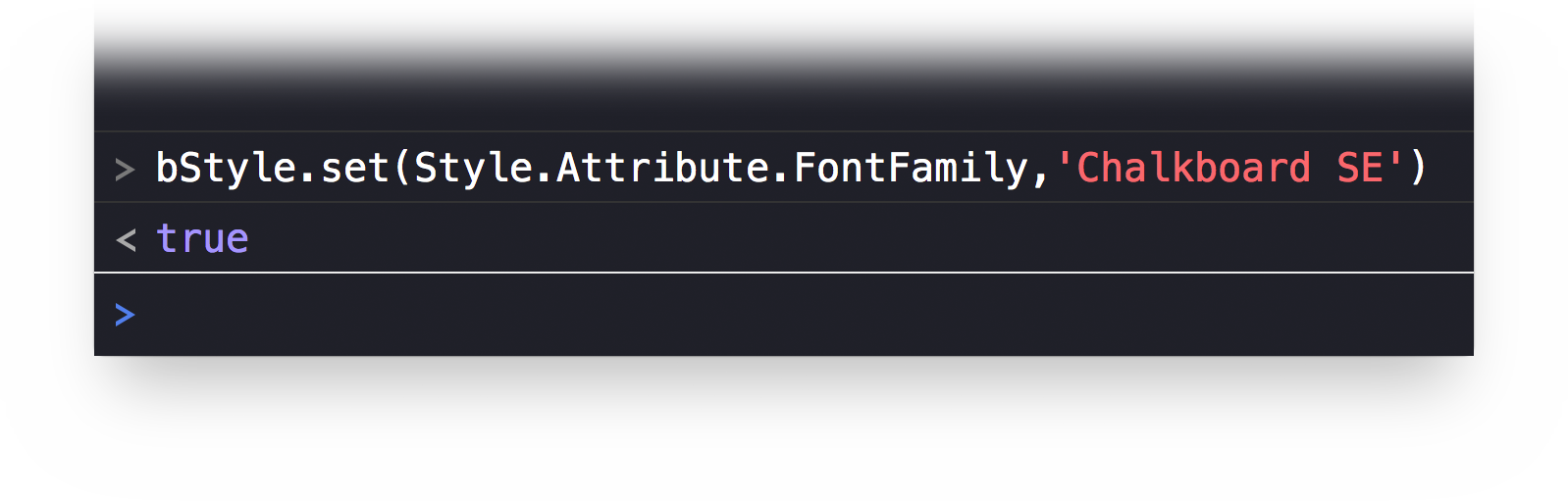
bStyle = document.outline.baseStylebStyle.set(Style.Attribute.FontFamily,'Chalkboard SE')
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script execution will be the boolean value of true.
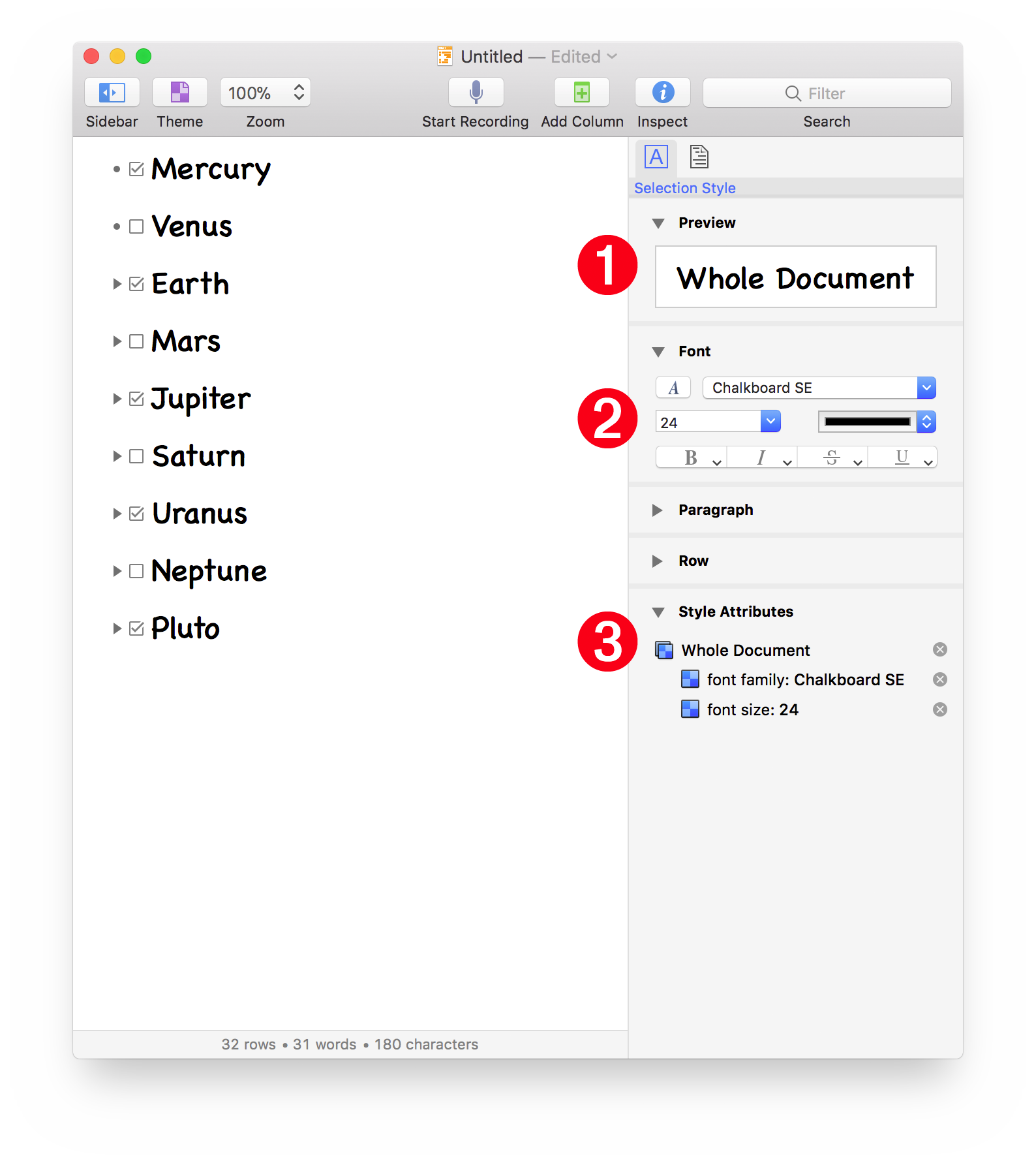
Let’s examine the visual changes to the document brought on by changing the values of some of the attributes of the base style.
Document Style Inspector
The outline document window provides the means for viewing and editing all of the attributes of any style, including the Whole Document or base style.
In the document window toolbar, press the Inspect button to reveal the Inspector sidebar on the right side of the window. These are the three sections pertinent to the changes we’ve made so far:
1 Preview • A view showing the name of the style with the attributes applied to it.
2 Font Settings • The current values for the Font attributes, including font family and size.
3 Style Attributes • A summary of the currently non-default values for the Whole Document or base style. The attribute settings can be edited in this pane as well.
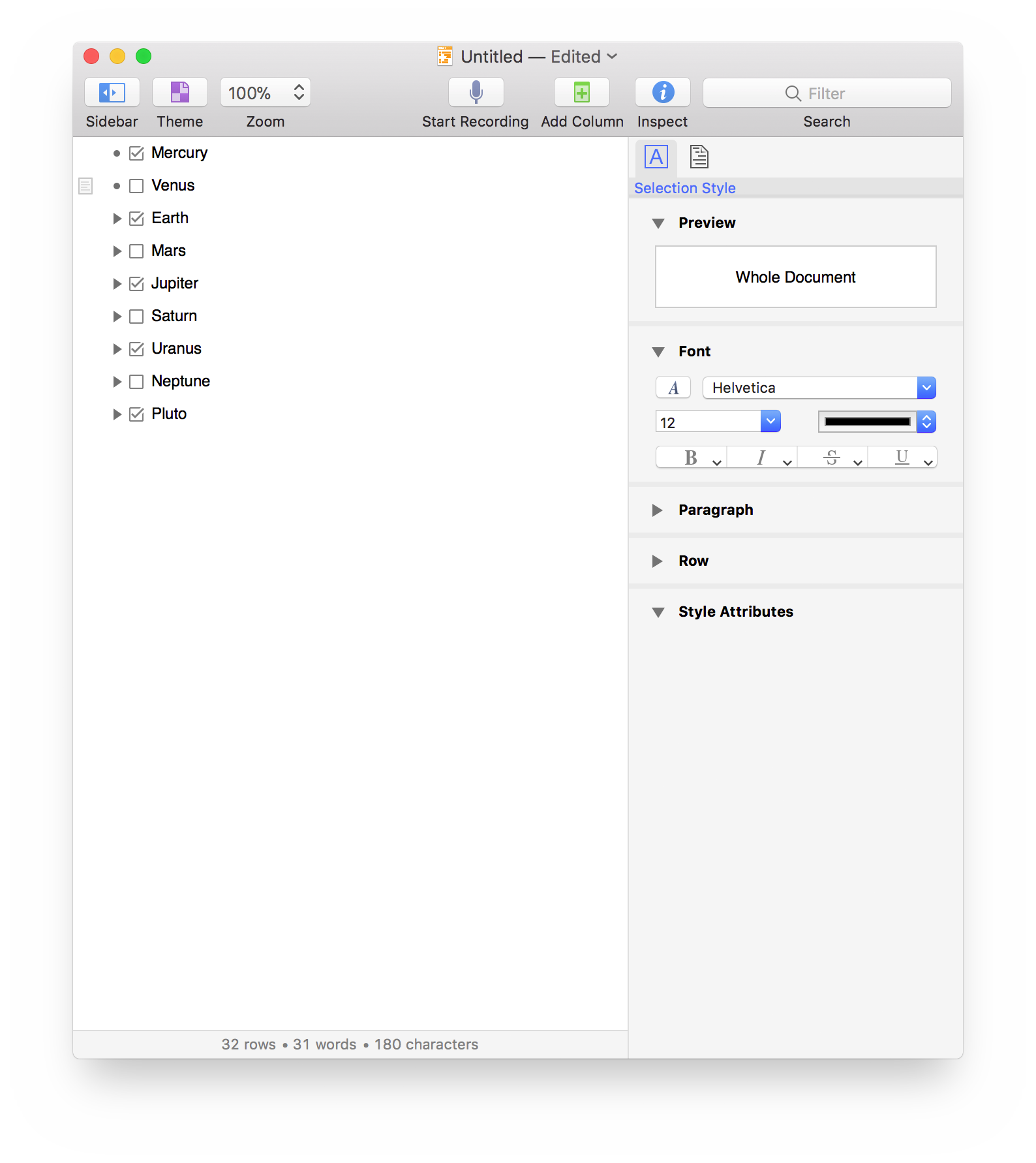
Back to Normal (default)
To restore the value of the changed attributes to their default values, we will use the clear() method of the Style class.
Set Base Style Attributes to Defaults
bStyle = document.outline.baseStylebStyle.clear()
| DO THIS ► | In the console window, enter and run the previous example script by pressing the Return key. |
The result of the script execution will be the return of all changes back to the default values of the base style.
What’s Next?
In the next section (Level Styles) we’ll learn how to apply styling to rows based upon their place in the outline hierarchy.