Plug-In Forms: Validation
Plug-In Forms (Action Forms) provide the means for the user to provide the script with the data and decisions necessary for the script to accomplish its automation task. Because a form may incorporate both the use of input and selection elements, it may be necessary to ensure that the data or selections fit within certain criteria before proceeding with the script’s execution. For example, does text input contain only alpha-numeric characters?
The validate property of the Form class contains a function that is used to control the enabling of the form’s approval button by checking the user provided data or selections. If the function returns a value of true, the button is enabled, otherwise the button is disabled by default.
(⬇ see below ) The form dialog. Note that the approval button is disabled until the content of the various elements matches required values.
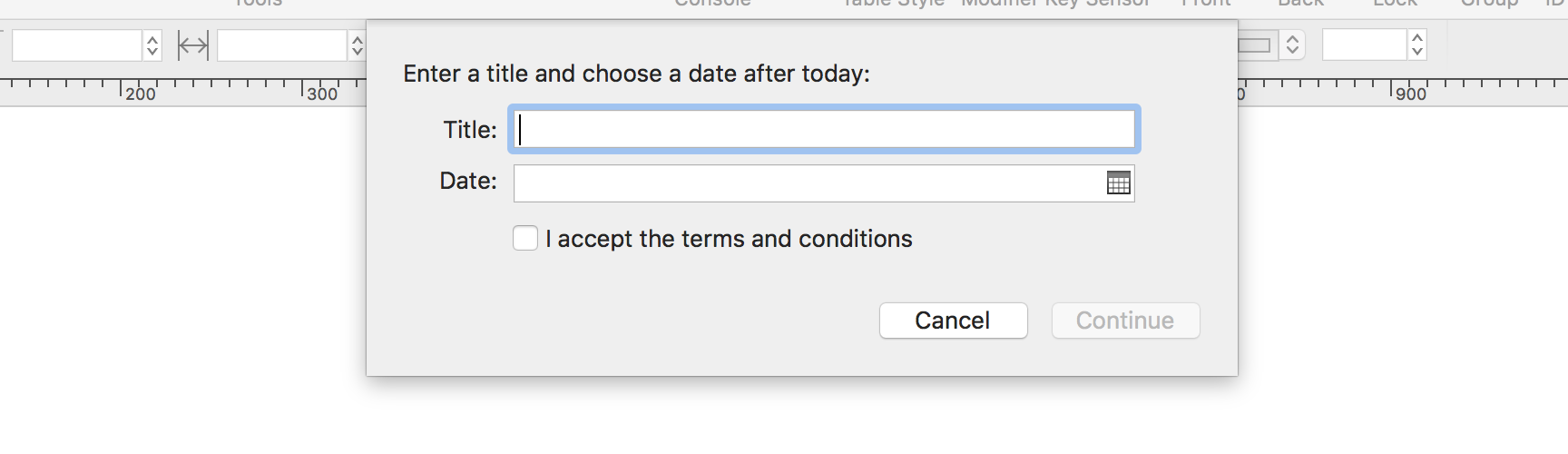
The form validation function is called when the dialog is displayed and every time the user interacts with its form elements, such as when text is entered in a text input field or a checkbox is selected or deselected.
When the form validation function is called, it is passed a JavaScript object representing the Form instance. The value of the form’s values property is a record of key:value pairs representing the identifier and current value for each of the fields in the form dialog. Omni Automation scripts parse this object record and use the retrieved data to determine the response provided by the function.
Form Instance Properties
fields (Array of Form.Field r/o) • The current Field instances in the form, which will be visible to the user entering input.
validate (Function or null) • A function to check whether the entered values are acceptable. The form to validate is passed as the argument and the function is expected to return a boolean result or null to perform default validation. If an Error is thrown, it’s message will be displayed in the form as the reason for validation failure. Note that the validation function may add or remove fields and update entries in the values object (which will cause the interface to be updated). This is called any time the user edits values, or a field is added or removed. If no validate function is specified or it returns null, some per-field default validation will be performed (see Form.Field.Option. If the validate function returns a boolean result, no default validation will be performed.
values (Object r/o) • An object with the collected values for each field, stored under the key for that field.
There are three options that may be returned as the result of the validate function:
Returning a Boolean value of true will cause the approval button to be enabled in the form dialog.
Returning a Boolean value of false will cause the approval button to remain disabled in the form dialog.
The text of an error message thrown in the validation function will be displayed in the form dialog. This technique can be used to provide information to the user as to why the current data settings don’t meet the script’s requirements. (Throwing an error in the function is examined in more detail later.)
Example Form Validation
The example code detailed below, demonstrates the use of the Form class validate function to make sure that the user has interacted with the dialog to provide data or selections that meet the scripts criteria, which in this case is:
- A title, comprised of one or more characters
- A date later than the current date
- Approval of the checkbox
NOTE: this example action doesn’t perform any actions, it is intended to be a simple example of form validation.
NOTE: This page contains interactive script examples that are executed only with your approval. See the section on Script Security for details about allowing the execution of remote scripts.Form Validation Example
// DIALOG PROMPT AND OK BUTTON TITLEformPrompt = "Enter a title and choose a date after today:"buttonTitle = "Continue"// CONSTRUCT THE FORMinputForm = new Form()// CREATE FORM ELEMENTS: TEXT INPUT, DATE INPUT, AND CHECKBOXtextField = new Form.Field.String("title","Title")dateField = new Form.Field.Date("date", "Date")checkbox = new Form.Field.Checkbox("checkbox","I accept the terms and conditions",false)// ADD THE ELEMENTS TO THE FORMinputForm.addField(textField)inputForm.addField(dateField)inputForm.addField(checkbox)// DISPLAY THE FORM DIALOGformPromise = inputForm.show(formPrompt, buttonTitle)// VALIDATE FORM CONTENTinputForm.validate = function(formObject){// EXTRACT VALUES FROM THE FORM’S VALUES OBJECTtextValue = formObject.values['title']//--> "Report"dateObject = formObject.values['date']//--> "2019-01-19T08:00:00.000Z"checkValue = formObject.values['checkbox']//--> trueconsole.log(JSON.stringify(formObject.values))//--> {"checkbox":true,"title":"Report","date":"2019-01-19T08:00:00.000Z"}// HAS TEXT BEEN ENTERED IN THE INPUT FIELD?textStatus = (textValue && textValue.length > 0) ? true:false// IS THE PROVIDED DATE LATER THAN NOW?dateStatus = (dateObject && dateObject > new Date()) ? true:false// ALL CONDITIONS MUST BE TRUE TO VALIDATEvalidation = (textStatus && dateStatus && checkValue) ? true:false// RETURN THE VALIDATION STATUSreturn validation}
26-51 The validation function called on the Form instance. The pass-through variable formObject in the validation function will contain an object reference to the form as it is currently displayed in the dialog.
28, 31, 34 The current values of the form elements is retrieved from the form object by parsing the record that is returned as the value of the values property of the form object. The individual form elements are referenced using the unique keys used to create the individual elements. Note that the value of the checkbox is a boolean value of either true or false.
37 Using the stringify method of the JSON class to log the contents of the form’s values record. Note that this method does not return a result for values that are objects.
41 A JavaScript conditional ternary operator statement that creates a variable with a value of either true or false based upon the result of the condition enclosed within the parens. In this example there are two conditions which must be met in order to return a value of true: if there a text object returned and is its length (number of characters) greater than 0? If yes, then return true, otherwise return false.
44 A ternary operator that checks to see if there is a date object within the passed form’s values record, and that the date is greater than the current date.
47 a ternary conditional statement that returns a value of true if all of the values within the parens are true, otherwise if any of them is false, a value of false is placed within the variable: validation
50 The boolean value of the previous statement is returned as the result of the validation function. If the value is false, the approval button in the displayed form dialog will remain disabled, otherwise if the returned value is true, the button will be enabled, ready for the user to select.
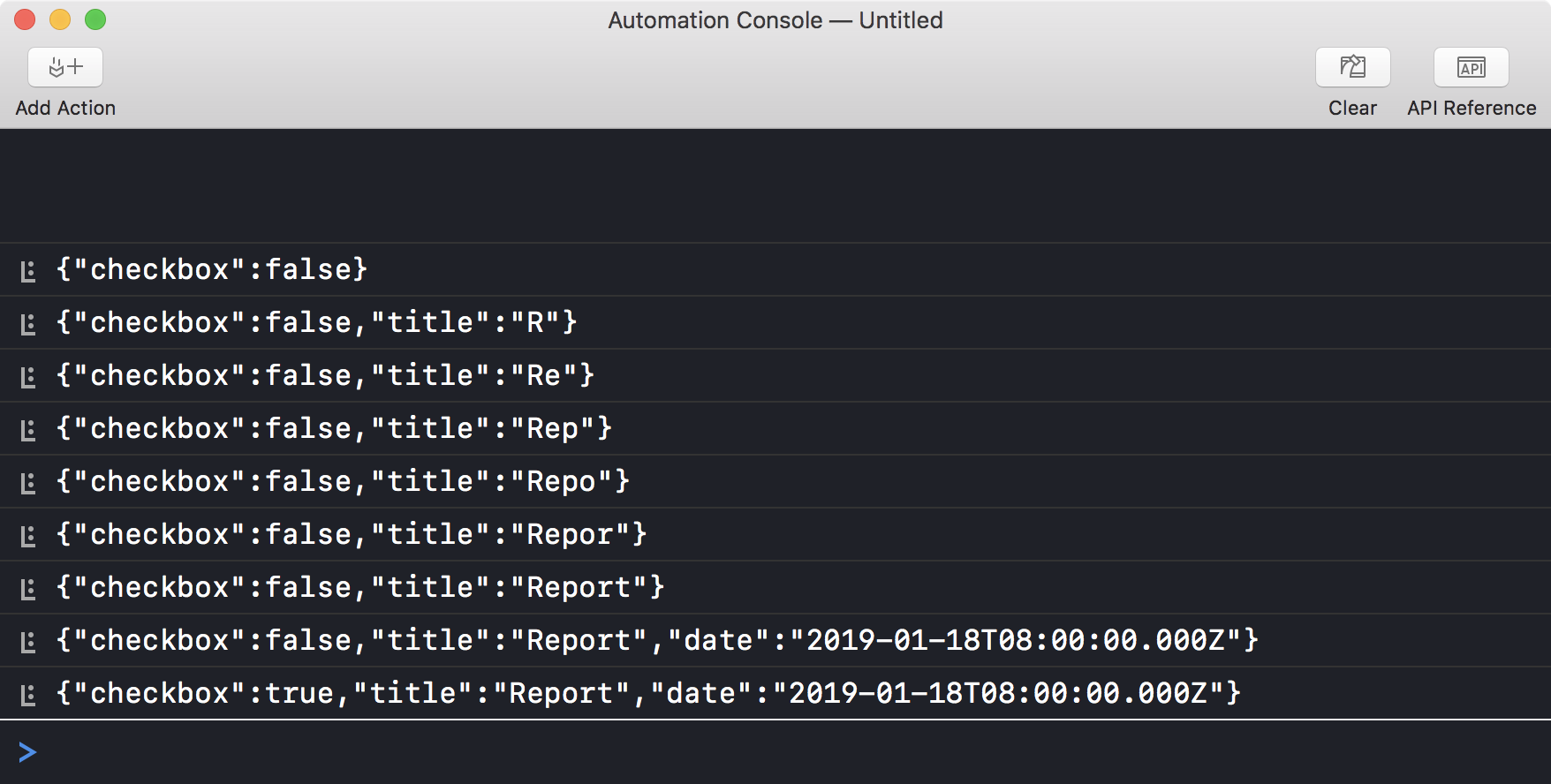
The illustration below shows the logging statements in Console window during the user’s interaction with the dialog:
(⬇ see below ) The console window showing the validation log. Note the last entry reflects the dialog state before the approval button is pressed.
Displaying Error Messages in the Dialog
When designing your form dialogs, you may want to the provide the user with feedback if entered or selected data does not meet the criteria necessary for the script to perform its tasks correctly. You can provide feedback by returning an error string instead of a boolean value.
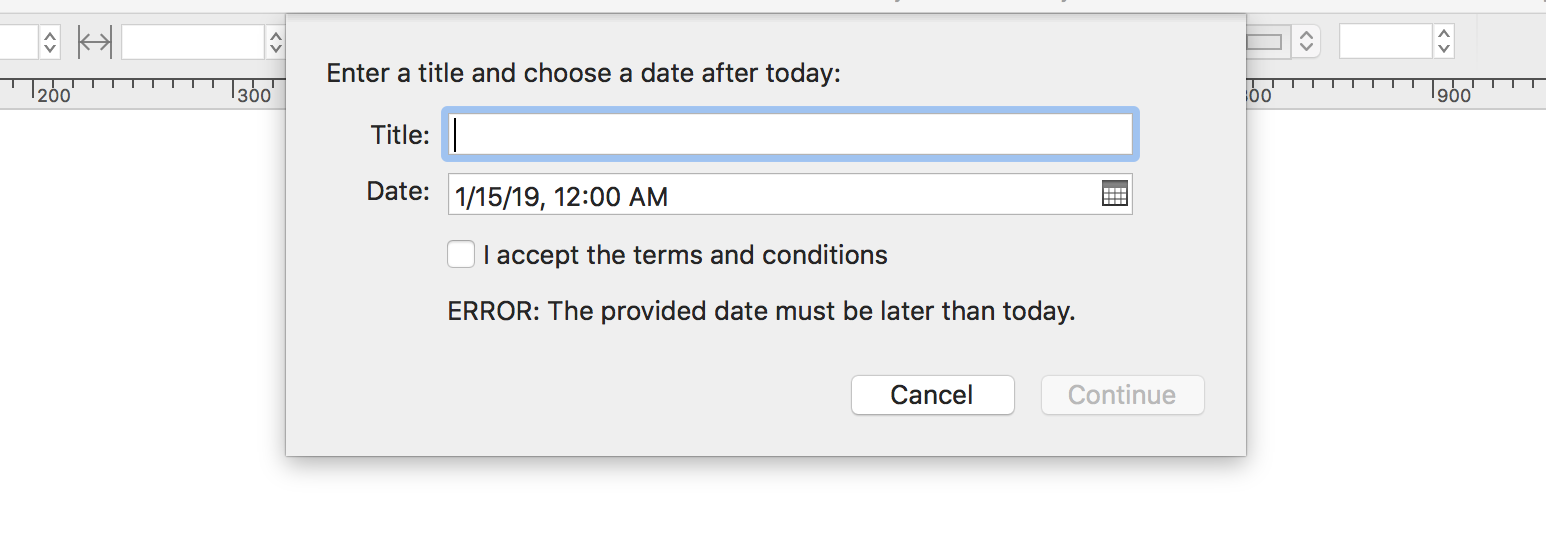
The example below would replace the ternary operator in line 44 of the example action shown above. If the user enters a date earlier than the current date, the form dialog window will display the error text at the bottom of the dialog.
(⬇ see below ) The error string is displayed as feedback to the user:
Here is a date validation that ensures that the provided date is later than today:
Date Validation
// IS THE PROVIDED DATE LATER THAN TODAY?if (dateObject){if (dateObject >= new Date(new Date().setHours(24,0,0,0))){return true} else {throw "ERROR: The provided date must be later than today."}}
Next we’ll examine an advanced use of the form validation function to make interactive menus.
Follow-On Menus
A Follow-On Menu is one whose appearance and/or contents change based-upon the selection of another menu in the form dialog. In the video below, the second menu (displaying the city names) is a follow-on menu to the one at the top of the form dialog:
|
|
While the creation of the form and its initial elements are done prior to the calling of the show() function, the logic and manipulation of the dialog elements occurs within the form’s validation function. Therefore, such code must include checks for the state of the various form elements, as the validation function gets called each time a form element is edited.
Note that in the case of follow-on menus, while the contents of a menu element cannot be edited, the menu itself can be replaced by another whose contents are different than one it replaces. To delete a menu, the removeField(…) function is called on the form object using the form menu to be deleted as the method’s parameter.
IMPORTANT: form elements cannot be reused (shown then hidden then shown again). Instead, new versions of the element must be created as replacements.
The example plug-in (shown below) displays a form dialog whose second menu is a follow-on of the first (topmost) menu:
Follow-On Menus
/*{"type": "action","targets": ["omnigraffle","omniplan","omnifocus","omnioutliner"],"author": "Otto Automator","identifier": "com.omni-automation.all.follow-on-menus","description": "Displays a form with follow-on menus.","version": "1.3","label": "Follow-On Menus","shortLabel": "Menus","paletteLabel": "Menus","image": "filemenu.and.cursorarrow"}*/(() => {const action = new PlugIn.Action(async function(selection, sender){// DIALOG PROMPT AND OK BUTTON TITLEformPrompt = "Select a continent and a city:"buttonTitle = "Continue"// CONSTRUCT THE FORMinputForm = new Form()continentMenu = new Form.Field.Option("continent","Continent",[0, 1, 2],["Africa","Asia","Europe"],0)AfricanCities = ["Lagos, Nigeria","Cairo, Egypt","Nairobi, Kenya","Addis Ababa, Ethiopia"]AfricanCitiesIndexes = [0, 1, 2, 3]AsianCities = ["Toyko, Japan","Dehli, India","Shanghai, China","Karachi, Pakistan"]AsianCitiesIndexes = [4, 5, 6, 7]EuropeanCities = ["Istanbul, Turkey","London, England","Paris, France","Moscow, Russia"]EuropeanCitiesIndexes = [8, 9, 10, 11]allCities = AfricanCities.concat(AsianCities).concat(EuropeanCities)AfricanCitiesMenu = new Form.Field.Option("city","City",AfricanCitiesIndexes,AfricanCities,AfricanCitiesIndexes[0])// ADD THE ELEMENTS TO THE FORMinputForm.addField(continentMenu)inputForm.addField(AfricanCitiesMenu)// VALIDATE FORM CONTENTinputForm.validate = function(formObject){continentIndex = formObject.values["continent"]cityIndex = formObject.values["city"]if(typeof cityIndex != "undefined"){if (continentIndex == 0 && !AfricanCitiesIndexes.includes(cityIndex)){inputForm.removeField(inputForm.fields[1])} else if (continentIndex == 1 && !AsianCitiesIndexes.includes(cityIndex)){inputForm.removeField(inputForm.fields[1])} else if (continentIndex == 2 && !EuropeanCitiesIndexes.includes(cityIndex)){inputForm.removeField(inputForm.fields[1])}}if (formObject.fields.length == 1){switch(continentIndex){case 0:AfricanCitiesMenu = new Form.Field.Option("city","City",AfricanCitiesIndexes,AfricanCities,AfricanCitiesIndexes[0])inputForm.addField(AfricanCitiesMenu)break;case 1:AsianCitiesMenu = new Form.Field.Option("city","City",AsianCitiesIndexes,AsianCities,AsianCitiesIndexes[0])inputForm.addField(AsianCitiesMenu)break;case 2:EuropeanCitiesMenu = new Form.Field.Option("city","City",EuropeanCitiesIndexes,EuropeanCities,EuropeanCitiesIndexes[0])inputForm.addField(EuropeanCitiesMenu)}}return true}// DISPLAY THE FORM DIALOGformObject = await inputForm.show(formPrompt, buttonTitle)// RETRIEVE CHOSEN VAUEScityIndex = formObject.values["city"]chosenCity = allCities[cityIndex]// PERFORM TASKSencodedCityName = encodeURIComponent(chosenCity)urlStr = 'maps://maps.apple.com/?address=' + encodedCityNameurl = URL.fromString(urlStr)url.open()});return action;})();
14-15 Declare variables containing the dialog prompt and approval button title.
18 Create an instance of the Form class and store it in the variable: inputForm
20-26 Create the primary menu (field) that will display some continent names.
28, 30, 32 Declare variables that hold arrays containing the names of some cities within the continent.
29, 31, 33 Declare variables that hold arrays of the indexes corresponding to the city names.
34 Create a single array of all of the city names, placed in a numeric order matching their corresponding indexes, and store the array in the variable: allCities
36-42 Create the secondary menu that corresponds to the first item (continent) of the primary menu.
45, 46 Use the addField(…) method of the Form class to add the instances of the primary and secondary menus to the created form object.
49 Use the show(…) method of the Form class to display the form dialog to the user. The result of the display is a JavaScript Promise.
52-100 The form’s validation handler that is called whenever the form is displayed or edited. The function contains the logic and statements for manipulating the display of the follow-on menu.
53, 54 Use the field object keys to retrieve the current indexes from the values object of the form passed into the validation function.
56-64 If the secondary (follow-on) menu exists, and it does not contain the cities for the currently selected continent, then remove the menu using the removeField(…) method.
66-100 If there is only one menu in the dialog, then adda follow-on menu based upon the current selection of the continent menu.
103-113 The form results are processed using the then(…) method on the JavaScript Promise that was the result of the dialog display.
105 The index of the chosen city is retrieved from the passed form’s values object using the secondary menu’s key.
106 The name of the chosen city is retrieved from the array of cities using the retrieved index, whose value matches the position of the city name in the array of city names.
109-112 The city name is URL encoded and appended to a URL string for performing a search using the built-in Apple Maps app. The string is converted into a URL object and is executed using the open( ) function of the URL class.
(⬇ see below ) The example action performed on the iOS platform:
|
|